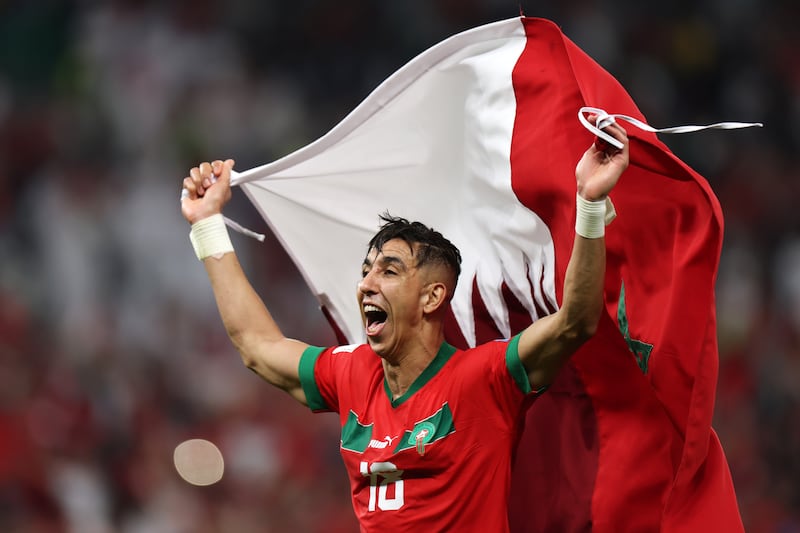
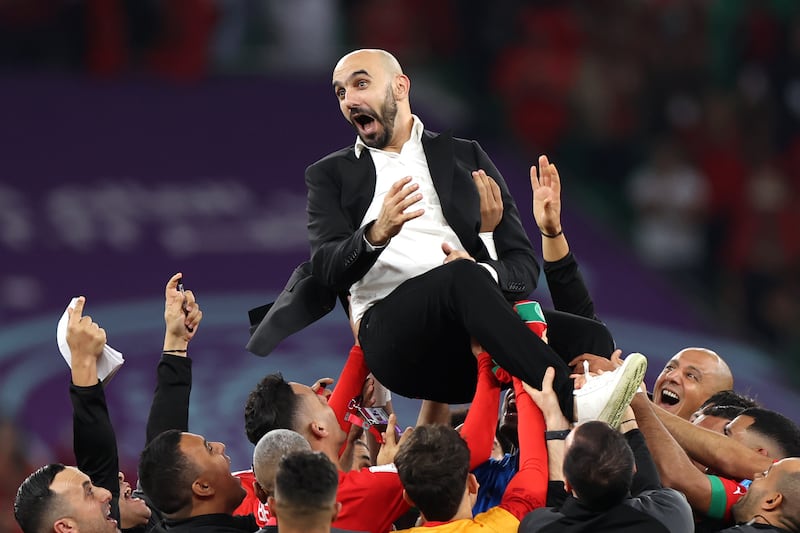
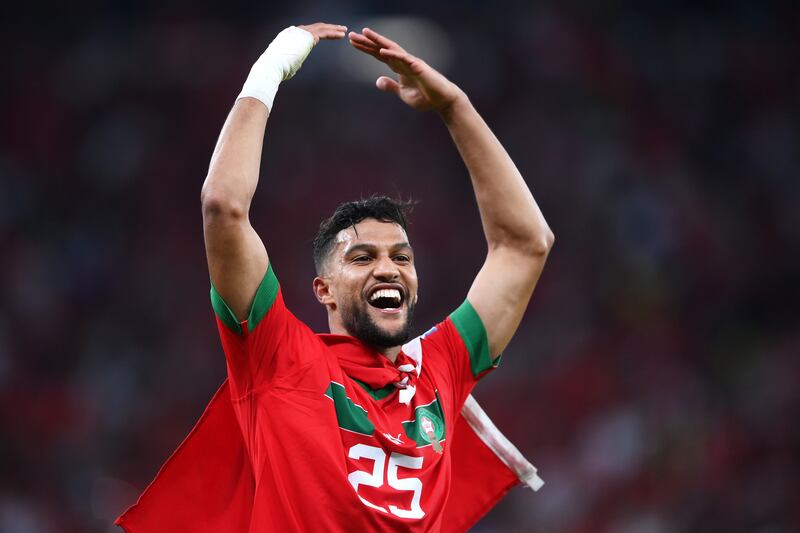
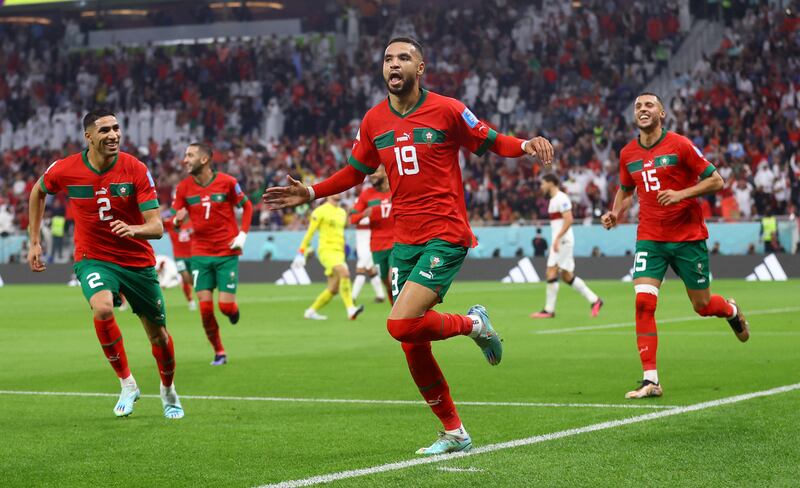
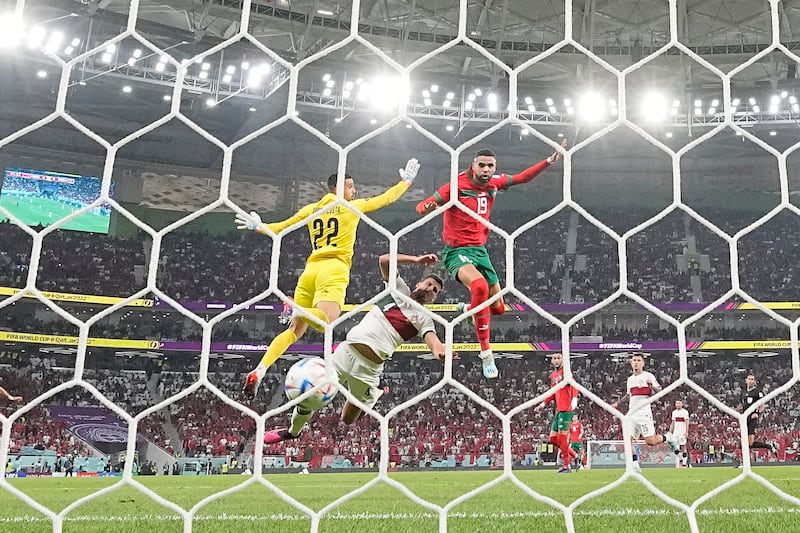
Morocco took centre stage this week after its football team became the first African team ever to reach the semi-finals of the World Cup, leaving admirers curious about Moroccan heritage and history.
While it has sparked a debate about identity but also about language as several players have said they have difficulty understanding each other due to different dialects in the country.
Local media reported the players even communicate mostly in English to avoid confusion.
This has raised eyebrows, especially after a video of Abdelhamid Sabiri, Morocco’s attacking midfielder, circulated online in which he said he finds it hard to express himself in Darija (Moroccan Arabic) because he speaks mainly Berber at home.
“My Arabic is not so strong and the language that I used to speak at home was not Arabic, it’s Berber and I don’t really understand the Darija dialect,” Sabiri said.
Most of the team members speak Berber and have been vocal about their backgrounds.
Munir El Kajoui, the team’s goalkeeper, has posed with the Berber flag on several occasions.
It is also hard for other Arab nations to fully understand the Moroccan dialect of Darija.
Morocco has in recent decades more fully embraced its African and Amazigh, as well as Arab, identity.
The team's historic World Cup knockout victory over Spain on Tuesday left fans across the Middle East and North Africa ecstatic at what they considered a victory for the entire Arab world.
The team is set to play against France in the semi-finals on Wednesday.
What language do they speak in Morocco?
Arabic is the official language of the country but it differs from traditional or literary Arabic.
Darija is spoken most across the country, which is known as the “street Arabic” of Morocco.
Darija Arabic is unique to Morocco and is not widely understood by native Arabic speakers from the region.
Within Morocco, Darija differs from region to region, especially in the north compared to the rest of the country.
The second most-used dialect is Amazigh, which is the language of the Berbers, the indigenous people of Morocco.
France and Spain controlled Morocco in the early 1900s, and although Morocco gained independence in 1956 French is still widely spoken by Moroccans of all ages.
Spanish is spoken in the northern regions, where the influence of the Iberian Peninsula remains evident.
French is spoken almost everywhere in the country, as it is taught universally and serves as Morocco's primary language of commerce, economics, culture and sciences.
Are Moroccans African, European or Arabs?
Morocco has a rich cultural blend of Arab, Berber, Jewish, European and African influences.
The majority of Moroccans have Arab and Berber roots, as in other countries in the Maghreb region.
The nation has a population of nearly 35 million, split between Arabs, Arabised Berbers — who speak Arabic — and Berbers, who also inhabit parts of Niger and Mali, as well as the majority of North African countries, particularly Libya, Algeria and Tunisia.
The country is a member of the Arab League but its constitution says that all of these communities and backgrounds are what make the country we see today.
"[Morocco's] unity is forged by the convergence of its Arab-Islamist, Berber and Saharan-Hassanic [saharo-hassanie] components, nourished and enriched by its African, Andalusian, Hebraic and Mediterranean influences," the constitution says in the preamble.
Ecstatic Morocco fans celebrate victory on London's streets