Once abandoned, sleepy villages on the under-construction road from Oman to Saudi Arabia are coming back to life as residents hope for a more prosperous future.
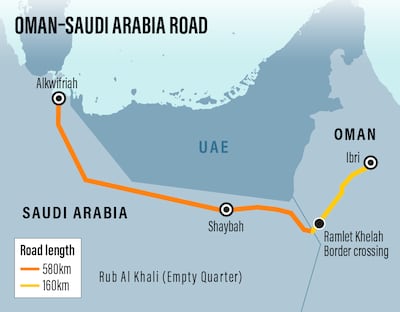
The motorway, more than 700 kilometres long, will start from Ibri, a town in south-west Oman, and end in Alkwifriah in Al Ahsa, eastern Saudi Arabia. It is expected to be finished by the end of the year.
The road passes straight through the Rub Al Khali desert, known as the Empty Quarter, which spreads across Oman, Saudi Arabia and the UAE. The section of the road in Oman is about 160km long, and about 580km of it will be in Saudi Arabia.
Once completed, the road will save more than 16 hours of travel time between the two towns at each end. The existing 1,600km road linking the two nations also cuts through the desert, but via a much longer route. It was built more than 40 years ago.
Ibri is home to Bat, a Unesco world heritage site dating to the third millennium BC. It has monumental stone towers and ancient tombs and was once a thriving a trade route that linked Oman and the rest of Arabia.
For the last two decades, nearby villages such as Wadi Sharsah, Al Ayn and Khutm were being abandoned as young people moved to cities including Muscat, Sohar and Salalah in search of a better life.
“I was planning to move to Muscat if I found a job there, just like the rest of the young generation here who were moving out from Wadi Sharsah village looking for brighter future. But I am now excited about the new road,” Khalfan Al Siyabi, 25, told The National.
Mr Al Siyabi, who has been looking for a job for two years, said he could not wait for the construction work to finish so he could start a business. “With the help of my brothers working in Muscat, I am going to buy a bus and use it to transport pilgrims to Makkah once the road is completed,” he said.
Another three young men, all in their twenties, were planning to start a tour company to introduce Saudis to the prehistoric site of Bat.
"They will come from Saudi Arabia and even from Muscat and the rest of the Gulf to see the old Bat civilisation and we will be here to show them around,” Said Al Abri, 26, from the village of Al Ayn in Ibri, told The National.
“It is going to be very promising in a year or so from now,” he said.

The motorway was originally scheduled for completion in 2014, but was delayed because of technical and financial issues.
Ahmed Al Saifi, 56, has already taken matters into his own hands after years of barely managing. He has begun work to convert his land at the side of the road into a petrol station.
“Travellers will need a petrol station since it is going to be a long journey to Saudi Arabia. My brother is also going to build shops and a restaurant on his land as a stopover for travellers,” said Mr Al Saifi, a landowner in Khutm village.
“All this will bring new life and prosperity to the villages here. We are very excited about it.”

Saudi Arabia is in the midst of an ambitious economic development plan to wean the economy off oil. Last year Oman introduced measures to boost its finances. It also recently asked the International Monetary Fund for assistance to rein in its debt.
In July, Oman’s Sultan Haitham bin Tariq travelled to Saudi Arabia on his first foreign visit since he took over in January last year after succeeding Sultan Qaboos bin Said, who had ruled for 50 years.
Last week, Saudi Investment Minister Khalid Al Falih visited Oman to discuss opportunities in both countries. One of the topics was a plan to boost trade on the new motorway.
Both countries were hit hard by the coronavirus crisis and low oil prices last year, and are keen to attract foreign investment as part of their reform efforts.


