When I took part in the Delphi Economic Forum in Greece this month, discussions centred on the prerequisites for transformative corridor projects in the Middle East, such as the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, the Belt and Road Initiative and the Iraq Development Road. Security, political stability and an end to wars emerged as essential conditions.
However, critical questions were raised at the forum. Do these major projects clash with each other, or can they be complementary? Can trust-building among political actors bridge gaps and strengthen incentives for co-operation? And does US President Donald Trump have enough commitment to support, follow up and accelerate the launch of Imec?
Mohammed Baharoon, director general of the Dubai Policy Research Centre, and I represented the UAE in a session on Mediterranean-Gulf connectivity and the added value of corridor projects in deepening this connectivity. Our engagement highlighted how current geopolitical challenges have reshaped the momentum and feasibility of such initiatives, including Imec.
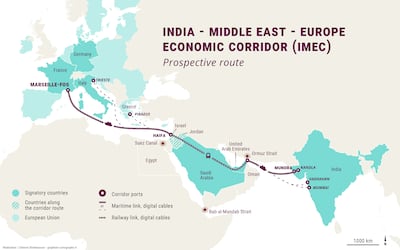
In general, the tragic war in Gaza has stalled the project’s momentum, as envisioned at its launch during the G20 Summit in New Delhi in September 2023. This war and the significant regional shifts since October 7 that year highlight the need for a reassessment to broaden participation in Imec and other such transformative mega projects. Improved Syrian-Iraqi relations could represent a significant step towards better integration of the two countries – as well as Lebanon, and perhaps even Gaza – into these corridors.
Imec gives economic diplomacy a more influential role in shaping the prospects of international relations, directing priorities and resources towards greater co-operation and economic interests rather than conflict. However, geopolitics is far from absent. The Gaza war and the resulting escalation between Israel and Iran, for example, were clear evidence of this. Instability also derails progress: the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, for instance, faltered largely due to political and social instability in Pakistan.
Among the challenges this project faces is the question of who will fund the tens of billions of dollars needed to improve existing infrastructure and address gaps remains unanswered. Imec requires more than 2,000 kilometres of railway, and large parts of it still need to be built in the Middle East’s rough terrain. For example, the shipping route from Haifa in Israel to Greece passes through waters disputed with Turkey, which is not part of the project.
Ankara’s objections to the project could become more vocal following the shift in Syria with the fall of Bashar Al Assad’s government last December and the subsequent rise in Turkish influence in the country. The exclusion of Egypt, Iraq and Oman from Imec could also pose some challenges to the project.
Therefore, the UAE advocates a more pragmatic and sustainable approach that considers projects and initiatives such as BRI, Imec and the Iraq Development Road (which includes the UAE, Qatar, Iraq and Turkey) as complementary rather than confrontational. This inclusive view offers the most practical and sustainable path forward.
While Turkey is apprehensive about Imec, which does not pass through its territory, Ankara’s involvement in the Iraq Development Road will determine whether this project competes with or complements Imec. Turkey’s role will also determine the extent to which the Iraq Development Road supports China’s BRI.
Chinese experts have so far expressed scepticism towards the infrastructure proposals associated with Imec, criticising what they see as a familiar US pattern of overpromising and underdelivering.
While Imec struggles to compete with BRI – a decade-old framework involving about 150 countries – it aligns with US efforts to empower a select group of “technically and financially capable” states. For China, Imec presents both a challenge and an opportunity. Just as the US has often downplayed BRI’s significance, Beijing may regard Imec with initial scepticism. However, the best-case scenario for all parties would be one of co-operation and constructive competition, rather than rivalry or confrontation.
It is evident that the UAE continues to pursue a multilateral foreign policy.
During his meeting with Chinese Premier Li Qiang in Abu Dhabi last September, President Sheikh Mohamed reaffirmed his country’s commitment as a strategic partner in BRI. He also emphasised that UAE-China relations represent a model of international co-operation rooted in diplomacy and dialogue.
China remains the UAE’s largest trading partner, with bilateral trade reaching $102 billion last year – marking a 7 per cent increase from 2023. In a first-of-its-kind development that will further deepen economic and tourism ties, China Eastern Airlines announced the launch of direct flights between Shanghai and Abu Dhabi, scheduled to begin today.
This move underscores Abu Dhabi’s strategic importance within the BRI framework. The emirate offers a supportive economic environment – bolstered by its advantageous geographic location, investor-friendly free zone policies and leadership in the energy and financial services sectors – making it an ideal hub for the global expansion of Chinese enterprises.
As economic ties deepen, with bilateral trade between the UAE and China projected to reach $200 billion by 2030, Abu Dhabi is steadily reinforcing its role as a gateway for Chinese investment into the Middle East and beyond. The emirate now hosts a significant number of Chinese companies operating in key sectors such as high tech, financial services, energy and industry.
Yet while China continues to deepen its BRI footprint, questions remain about the future of US-backed initiatives.
Mr Trump’s protectionist orientation has cast doubt on the depth of US commitment to Imec, which has been described as a potential catalyst for realising the long-envisioned Eurasian connectivity. While Mr Trump characterised Imec as “one of the greatest trade routes in history” during his meeting with Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi in February, expectations must be tempered by the need for realistic, adaptable approaches.
In the end, the success of Imec – and similar large-scale initiatives – depends on the ability of stakeholders to embrace a co-operative, win-win approach. Prioritising complementarity rather than rivalry is key to realising the full potential of regional connectivity.


