The US and India have agreed to a trade deal after months of wrangling. It is a deal that hinges on the world’s second-largest oil importer changing suppliers of crude. New Delhi has been one of the top buyers of Russian crude since Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine. This has prompted a backlash from Washington and Brussels who have accused India of enabling the Kremlin’s war machine. However, India has countered the accusations, saying it was operating on the basis of market economics, buying the cheapest barrels sellers had to offer. The trade deal, which gives India some tariff relief, is also tied to future purchases of Venezuelan crude. Since the US takeover of Venezuelan hydrocarbon assets, President Donald Trump has been pushing for buyers to channel purchases through US-controlled entities, effectively aligning energy flows with Washington’s geopolitical strategy and tightening its leverage over Caracas. Whether India acquiesces to this longer-term is doubtful.
In the region, Kuwait has taken the big step of finally allowing international oil companies to explore for oil and gas and help develop its hydrocarbon assets. Internal politics in Opec’s fifth-largest producer have previously restricted the participation of international oil companies in the country’s protectionist energy industry. However, this is changing. Neighbouring Iraq will also likely see foreign interest in its prized West Qurna 2 field - one of the world’s largest - with its majority-stake operator Lukoil poised to sell its assets to the US Carlyle group.
India-US trade deal
President Trump says India will buy more Venezuelan crude as part of the new US-India trade deal, linking energy purchases to tariff relief and reduced imports of Russian oil. Markets reacted to the broader deal, but New Delhi has not confirmed any binding oil commitment. Indian refiners cite practical hurdles such as payment channels, shipping insurance, sanctions compliance risk and the heavy quality of Venezuelan crude, all of which complicate a rapid restart. Supply is the bigger constraint. Venezuela’s output remains fragile and infrastructure-limited. Even with sanctions relief, production is expected to rise only gradually towards 1.2 million barrels per day by end-2026, leaving limited export headroom. India’s current crude diet is already optimised around discounted Russian and Middle Eastern barrels. Indian refiners need price incentives to move away from Russian Urals.
Bottom line: Venezuelan oil is politically useful in US-India diplomacy, but physical flows will depend on pricing, sanctions clarity and Venezuela’s ability to increase production. India might initiate a symbolic restart but is unlikely to commit to a large-scale pivot.

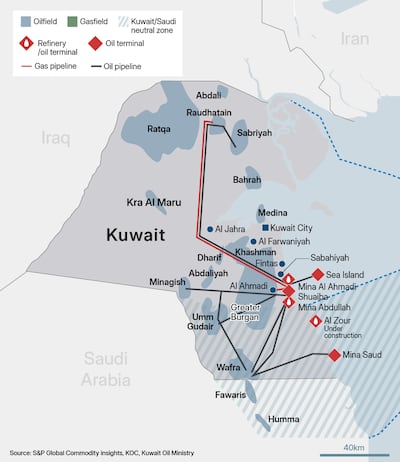
Kuwait opens to IOCs
Kuwait plans to invite international oil companies to develop new offshore discoveries and potentially the Neutral Zone with Saudi Arabia, targeting 4 million bpd capacity by 2035. Current output is about 2.6 million bpd, versus capacity near 3 million bpd, highlighting the scale of expansion needed. International partners have been invited to develop Nokhatha, which has 2.1 billion barrels of oil and 5.1 tcf of gas; Jazah, which has 120 million barrels of condensate and 1 tcf of gas; and Al-Jlaiaa, which has 800 million barrels of medium sweet crude.
Kuwait is nearing technical limits, with ageing fields such as Greater Burgan - Kuwait’s largest - running close to peak and Neutral Zone output vulnerable to political and operational disruption. Kuwait’s Gulf peers such as the UAE are already near their targeted capacity expansion goals and have invited international oil companies to co-develop oil and gas fields. Political changes in Kuwait have revived appetite for foreign expertise and capital.
Bottom line: Kuwait is shifting from defensive resource management to outward-looking growth, inviting foreign partners to reach its production capacity goals.
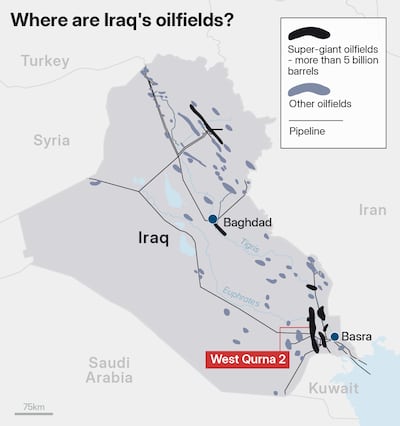
Iraq: West Qurna-2 after Lukoil’s exit
Lukoil’s conditional sale of overseas assets to Carlyle places Iraq’s West Qurna-2 - one of the country’s and world’s largest producing fields with output averaging 470,000 bpd - at the centre of a sanctions-driven ownership reshuffle. The deal requires US regulatory approval and remains uncertain, but Baghdad has already nationalised the asset to avoid disruption. Potential future operators could include Western majors already active in Iraq or Gulf-backed investors if Carlyle syndicates the asset.
Bottom line: The move signals a gradual unwinding of Russian energy influence in the Middle East, with Iraq’s flagship field becoming a test case for how sanctioned assets transition without supply interruption.
Big number
14 billion barrels
Estimated oil reserves in West Qurna 2
Happening this week
- World Governments Summit: February 3-5
- Kuwait Oil and Gas: February 3-5
- Libya's bid announcement: February 11
Chart of the week
Our top energy reads
The National produces a variety of newsletters across an array of subjects. You can sign up here.





